
Photoshop Color Replacement Tool Tutorial
In a previous tutorial, we looked at the Background Eraser and why it's one of the best tools in Photoshop for removing unwanted areas of an image. In this tutorial, we'll learn all about the Color Replacement Tool and how it enables us to change the color of an object in a photo without a lot of fuss or hassle.
You may be wondering what on earth a tool for erasing backgrounds has to do with a tool for changing colors, and the answer is, a lot! Both of these tools use the exact same technology for detecting the pixels in the image that need to be changed. The only difference is that one of them deletes pixels entirely, the other simply changes their color. In fact, they're so similar that if you've already read through the Background Eraser tutorial and understand how its various options work, learning about the Color Replacement Tool will seem a lot like déjà vu.
The Color Replacement Tool is not the most professional way to change colors in an image and won't always give you the results you need, but it usually works well for simple tasks and it's such an easy tool to use that it's worth giving it a try before moving on to more advanced and time consuming methods.
This tutorial is for Photoshop CS5 and earlier. If you're using Photoshop CS6 or Photoshop CC, you'll want to check out our fully updated Color Replacement Tool tutorial.
Selecting The Color Replacement Tool
The Color Replacement Tool was first introduced in Photoshop CS, and if you're using Photoshop CS or CS2, you'll find the Color Replacement Tool nested under the Healing Brush in the Tools palette. To access it, click and hold your mouse button down on the Healing Brush until a fly-out menu appears, then select the Color Replacement Tool from the menu.
In Photoshop CS3, Adobe changed things around a bit and moved the Color Replacement Tool in with the regular Brush Tool, so if you're using Photoshop CS3 or CS4 (which is what I'm using here), click and hold your mouse button down on the Brush Tool, then select the Color Replacement Tool from the fly-out menu:
With the Color Replacement Tool selected, your mouse cursor will change into a circle with a small target symbol in the center of it. As I mentioned, if you're familiar with the Background Eraser, this will look very familiar to you since both tools use the exact same cursor:
You can adjust the size of the circle directly from your keyboard using the bracket keys, which are found to the right of the letter P on most keyboards. Press the left bracket key ( [ ) to make the circle smaller or the right bracket key ( ] ) to make it larger. To change the hardness of the brush edges, just add the Shift key. Press Shift+left bracket ( [ ) to make the edges softer or Shift+right bracket ( ] ) to make them harder.
How The Color Replacement Tool Works
As you drag the Color Replacement Tool over your image, Photoshop continuously samples the color that's directly under the target symbol in the center of the tool's cursor. This is the color that will be replaced, and it will be replaced with your current Foreground color. Any pixels that fall within the larger circle surrounding the target symbol that match the color being replaced will have their color changed. For example, if you pass the target symbol over an area of blue in your photo and your Foreground color is set to red, any blue pixels that the larger circle passes over will be changed to red. There's some options we can set in the Options Bar to alter the behavior of the tool (which we'll look at shortly), but essentially, that's how it works.
You can see what your Foreground color is currently set to by looking at the Foreground color swatch near the bottom of the Tools palette. By default, it's set to black:

To change the Foreground color, simply click directly on the color swatch, then choose a new color from the Color Picker. I'll choose a green color, just for fun. Click OK to close out of the Color Picker when you're done:
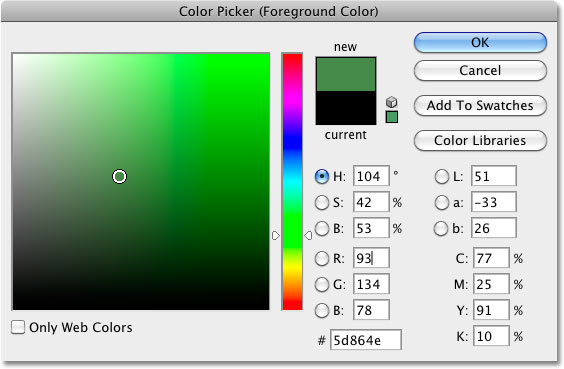
If I look again in my Tools palette, I see that the Foreground color swatch has changed to the new color. If I paint on an image with the Color Replacement Tool at this point, whichever color I drag the target symbol over will be replaced with green:

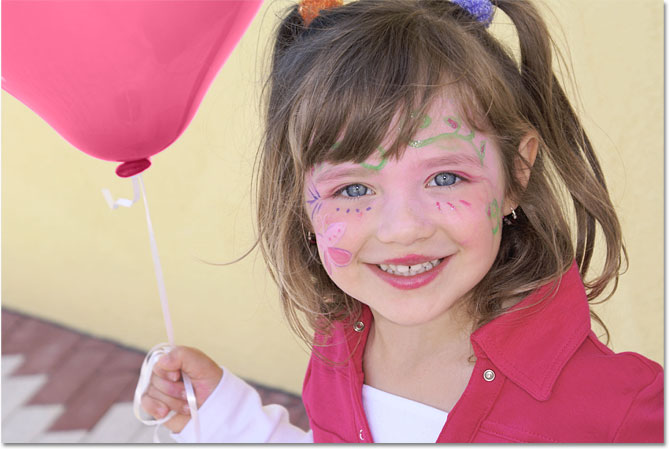
As an example, here's a photo of a young girl holding a balloon:
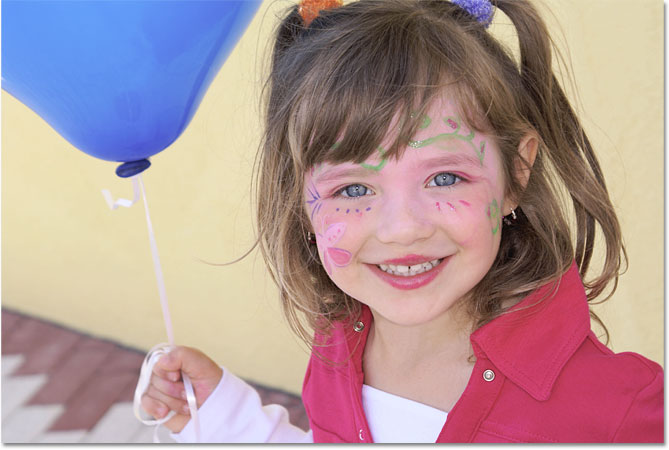

She may look happy with her blue balloon, but what she really wanted was a green balloon. As luck would have it, I just happen to have my Foreground color currently set to green, so let's see what we can do for her. With the Color Replacement Tool selected, I'll move the target symbol over the blue balloon in the image and click my mouse button. As soon as I click, two things happen. First, Photoshop samples the blue color under the target symbol so it knows which color to replace. Then, any blue pixels that fall within the larger circle surrounding the target symbol immediately change to green, since green is now my Foreground color:

To change the rest of the balloon to green, I just need to keep my mouse button held down and continue dragging the Color Replacement Tool over the remaining blue areas. As long as I keep the target symbol over the blue balloon and don't stray off into other areas of the image, which would cause Photoshop to sample a different color, only the blue color will be replaced with green:

If I accidentally move the target symbol outside of the balloon and over the yellow wall behind it, Photoshop samples the color of the wall and begins changing it to green as well:

If this happens, simply undo the last step by pressing Ctrl+Z (Win) / Command+Z (Mac), or undo multiple steps by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Z (Win) / Command+Option+Z (Mac) as many times as needed, then continue on.
Tolerance
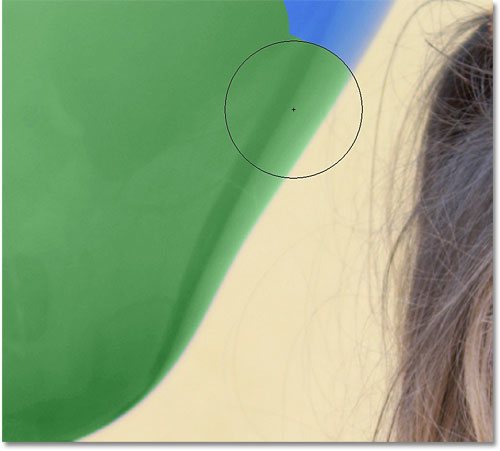
Everything seems to be going smoothly as I paint over the balloon until I get to the edges. If you look closely, you can see some faint blue fringing that the Color Replacement Tool is having trouble with:

I mentioned a few moments ago that there are several options available to us in the Options Bar for altering the behavior of the Color Replacement Tool, and one of these options is Tolerance. The Tolerance setting determines how different a color can be from the sampled color for Photoshop to replace it with the Foreground color. The default value is 30%, which is a good starting point. Unfortunately, it's not quite high enough in this case for Photoshop to be able to include the shade of blue right along the edges of the balloon.
I'll increase my Tolerance value to 50%, which will allow the Color Replacement Tool to affect a wider range of colors:

With a higher Tolerance value entered, I'll undo my last step and try again. This time, as I move along the edge of the balloon, the Color Replacement Tool is able to remove the blue fringing:

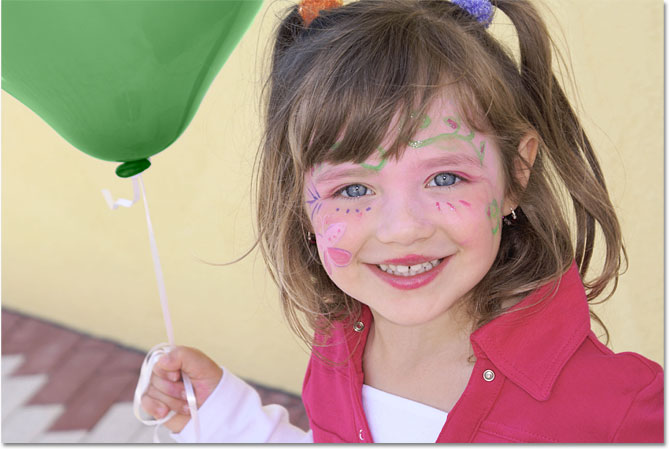
I'll finish painting over the remaining areas as our once blue balloon is magically transformed into green thanks to the Color Replacement Tool and a little boost in the Tolerance value:

Sampling Colors From The Image
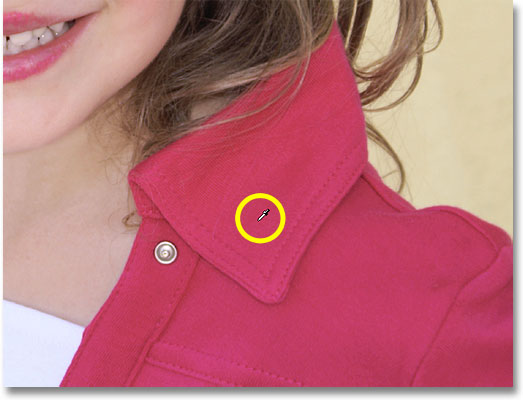
In the above example, I randomly chose a new color for the balloon from Photoshop's Color Picker, but I could just as easily have selected a color directly from the photo itself. To do that, with the Color Replacement Tool active, hold down your Alt (Win) / Option (Mac) key, which will temporarily switch you to the Eyedropper Tool (you'll see your cursor change into an eyedropper). Click on an area of the photo that contains the color you want to use. Photoshop will sample that color and make it your Foreground color. I'll click on the pinkish-red top she's wearing:

If I look at the Foreground color swatch in the Tools palette, I see that the color I clicked on has become my Foreground color:

With the color sampled directly from the image, I can paint over the balloon once again with the Color Replacement Tool to change its color:

Notice that even though we've essentially painted a color over top of the balloon, it retained its shiny, reflective appearance. If we had simply grabbed the regular Brush Tool and painted over it, the balloon would look like nothing more than a flat surface with no life to it. So how was the Color Replacement Tool able to keep the balloon's texture and reflections? For the answer to that, we need to look at more of the options in the Options Bar, which we'll do next!
The Blend Modes
The reason the Color Replacement Tool is able to paint a new color over an object or an area of a photo without losing the texture detail is because it uses blend modes to blend the new color in with the image. There's four blend modes to choose from (Hue, Saturation, Color, and Luminosity), all of which can be selected from the Mode option in the Options Bar. The default blend mode is Color:

If you've ever taken a Color Theory 101 class, you probably know that what most of us think of as the color of an object is really a combination of three things - hue, saturation and brightness. Each of the four blend modes we can select for the Color Replacement Tool will change which of these three aspects of the original color will be affected.
Hue: The Hue blend mode will change only the basic color itself. It will not change the saturation or brightness of the original color. This mode is useful for images where the colors are not very intense and will usually produce very subtle changes.
Saturation: The Saturation blend mode changes only the saturation of the original color. The hue and brightness are not affected. This is useful for reducing the intensity of a color, or even removing color completely.
Color: Color is the default blend mode and will change both the hue and saturation. The brightness will remain unchanged. This is the blend mode you'll use most often.
Luminosity: Finally, the Luminosity blend mode will simply match the brightness of the original color to the brightness of the new color. Hue and saturation are unaffected.
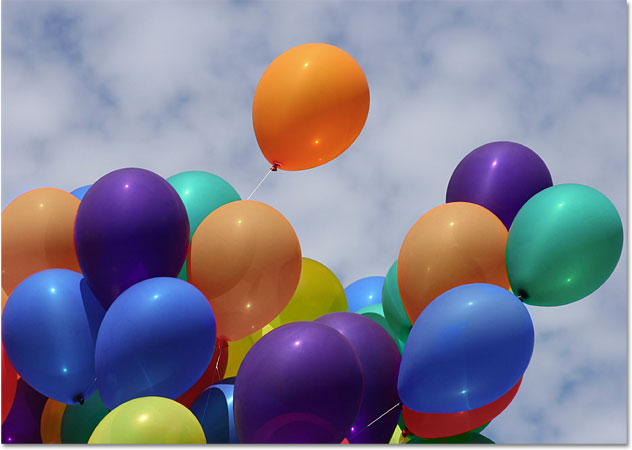
In this photo below, an orange balloon seems ready to split from the group and fly off on its own adventure into the sky:
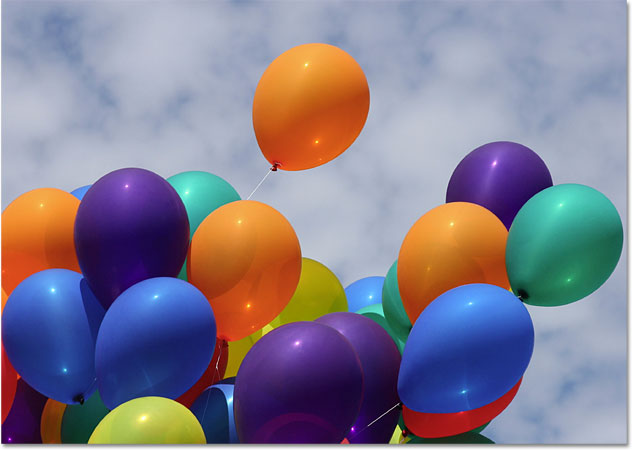

One way to make the balloon stand out even more from the others in the image might be to reduce the color saturation of some of the other balloons below it. I don't want to change the actual color of the balloons, just the intensity of them. To do that, with the Color Replacement Tool selected, I'll change my blend mode option in the Options Bar to Saturation:
If I wanted to completely desaturate the balloons, removing their color entirely, I'd set my Foreground color to either black, white or any shade of gray, but since I want a more subtle effect, I'll just sample one of the less saturated colors in the image by holding down my Alt (Win) / Option (Mac) key to temporarily switch to the Eyedropper Tool, then I'll click on the color I want. I'll choose a less saturated yellow. The color itself makes no difference since the Saturation blend mode won't change any of the original colors. It will only affect the saturation:
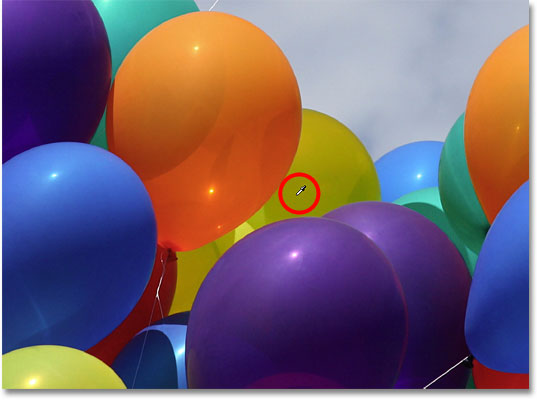

With a less saturated color now set as my Foreground color and my blend mode set to Saturation, I'll simply paint over any balloons that need their saturation level reduced, adjusting my brush size with the left and right bracket keys on the keyboard and changing the Tolerance value in the Options Bar as needed. Here, we can see the difference in color saturation as I paint over one of the other orange balloons:
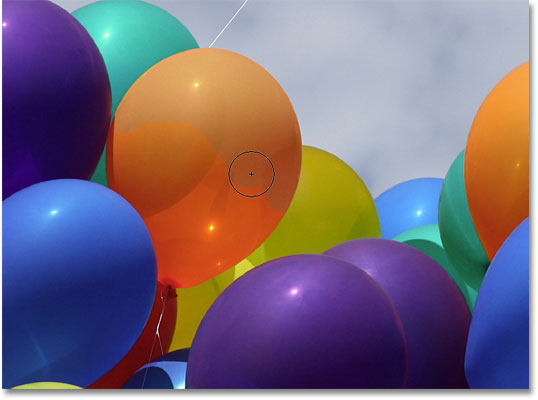

I'll continue painting over any other balloons that need their color saturation reduced. Here's the completed result:

The Brightness Problem
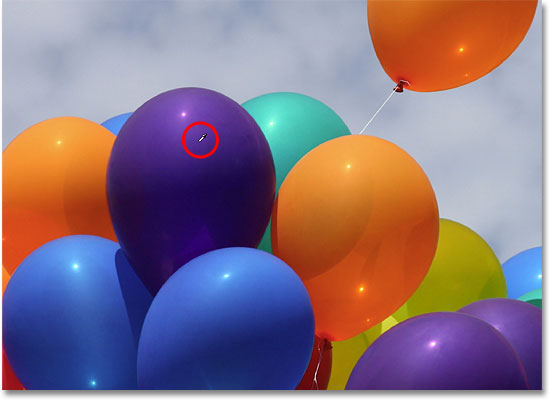
There's one situation, unfortunately, where the Color Replacement Tool tends to fail miserably, and that's when there's a big difference in brightness between the original color in the image and the color you want to replace it with. Let's say I wanted to replace the orange in that one balloon we've been focusing on with the dark purple color from one of the other balloons. From everything we've seen so far, it should be simple enough, right?
First, I'll set the colors in the image back to what they were originally by going up to the File menu at the top of the screen and choosing the Revert command. Then, with the Color Replacement Tool selected, I'll hold down my Alt (Win) / Option (Mac) key and click on one of the purple balloons to sample the color:

I'll set my blend mode in the Options Bar back to Color, the default setting. Then, I'll paint over the orange balloon to change its color to dark purple. Here's the result:
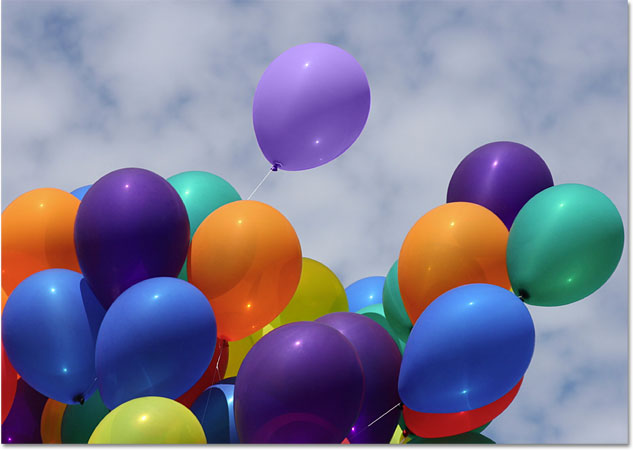

Hmm. It's definitely purple, but it doesn't quite look like the other purple balloons, does it? The problem is that it's much lighter than the other purple balloons, and that's because the original color of the balloon was much lighter than the dark purple color I sampled. The Color blend mode had no effect on the brightness. In fact, the only blend mode that does change the brightness is Luminosity, so let's try that one. I'll change my blend mode in the Options Bar to Luminosity:
I'll undo my steps to change the balloon back to its original orange color, and then, with my blend mode set to Luminosity this time, I'll try replacing the orange with dark purple:
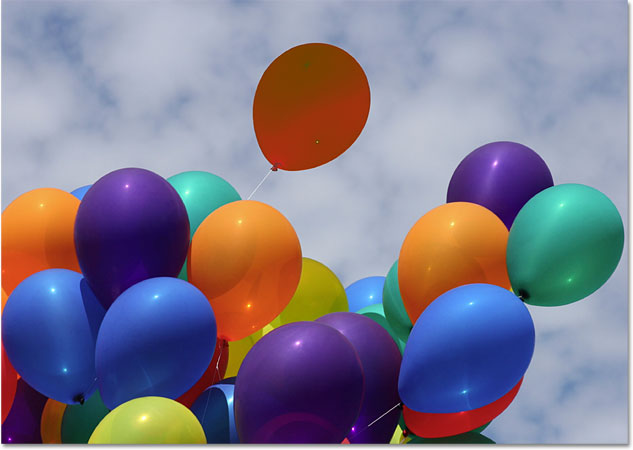

I think it's safe to say that things did not go well. The Luminosity blend mode definitely made the balloon darker, but it's still orange, and now most of the texture detail is gone! It barely looks like a balloon at all at this point, and this is the problem we face with the Color Replacement Tool. It works great for simple tasks where you only need to change the hue and/or saturation of a color, but if there's too much of a difference in brightness values between the original color and the new color, you'll probably want to try something else.
Sampling Options
Directly to the right of the blend mode option in the Options Bar is a row of three small icons. Each of these icons represents a different sampling option for the Color Replacement Tool, and they work exactly the same here as they do for Photoshop's Background Eraser. From left to right, we have Continuous (the default setting), Once and Background Swatch. Simply click on the icons to switch between them as needed:
These sampling options control how Photoshop samples colors in the image as you move the target symbol over them, or if it samples them at all. With Continuous selected, Photoshop continually looks for new colors to replace as you drag the Color Replacement Tool around. Any new color the target symbol passes over becomes the new color to replace. This is the setting you'll use most often and works best when there's a lot of variation in the color of the object.
With Once selected, Photoshop will only sample the color you initially click on regardless of how many other colors you drag over (as long as you keep your mouse button held down). This option works best if you're replacing a large area of solid color. You can also try the Once option if you find that Continuous is causing the Color Replacement Tool to bleed into other nearby areas and the Tolerance option doesn't seem to help.
Finally, you won't use it very often (if ever), but the Background Swatch setting will replace whatever color is currently set as your Background color. This option may prove useful if neither of the other two sampling options is working for you. Click on the Background color swatch in the Tools palette and select a color from the Color Picker that matches, as close as possible, the color in the image you want to replace. Try adjusting the Tolerance value if the color you chose wasn't quite close enough.
Limits
Another option that works exactly the same with the Color Replacement Tool as it does with the Background Eraser is Limits, which controls where Photoshop can look for colors to replace. The three choices are Contiguous, Discontiguous and Find Edges. Of the three, you'll really only ever use the first two:

The default setting for the Limits option is Contiguous, which means that the Color Replacement Tool can only change the color of pixels in the area the target symbol in the center of the cursor is touching. It won't affect pixels that match the sampled color but are separated from the target symbol by an area of a different color unless you physically move the target symbol into the new area. The opposite of this is Discontiguous, which allows the Color Replacement Tool to replace the color of any pixels that match the sampled color and fall within the boundaries of the cursor, whether those pixels are in the same area as the target symbol or not.
Anti-Alias
The final option for the Color Replacement Tool is Anti-alias, which is selected by default. Keep this option selected to smooth out the edges around the areas the Color Replacement Tool is affecting:
And there we have it! That's how to change the color of an object in a photo with the Color Replacement Tool in Photoshop! Check out our Photo Retouching section for more Photoshop image editing tutorials!